
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to understanding the intricate components that make up a vital feature of your property — the garage door.
Whether you’re seeking to make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance on your current garage door or a prospective buyer looking to invest in a new door, unraveling the anatomy of a garage door will equip you with the insights needed to navigate the market and ensure the optimal performance of this essential feature.
Table of Contents
What Are the Parts of a Garage Door?
Knowing the anatomy of a garage door enhances your ability to identify potential problems and take proactive measures to mitigate risks. Regular maintenance becomes a breeze as you recognize the signs of issues early on with your knowledge of how a garage door system works.
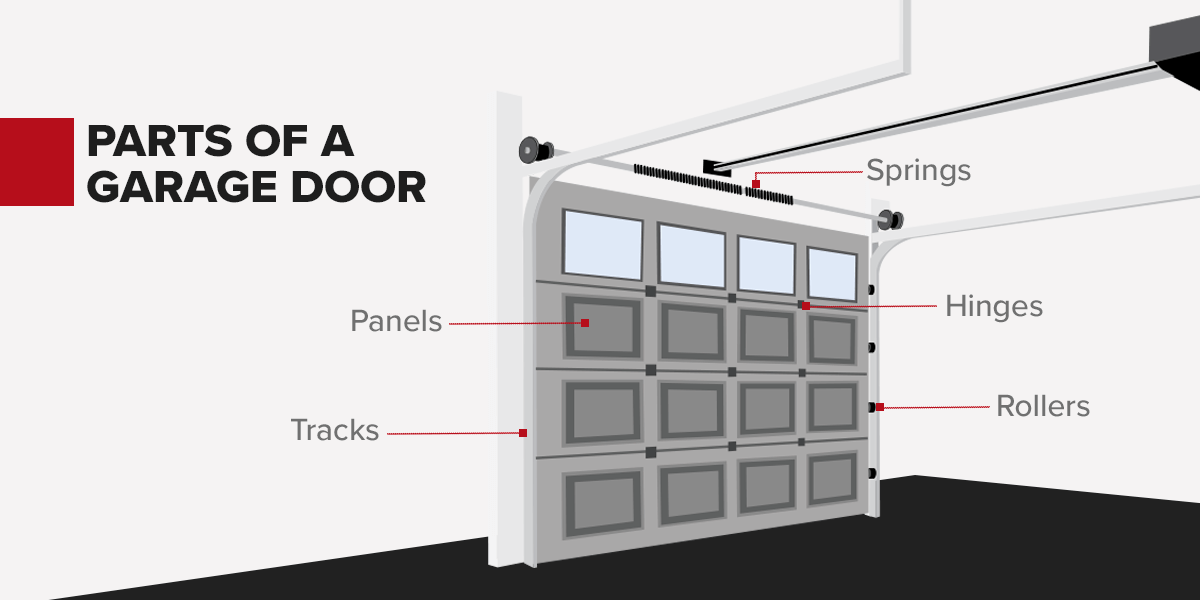
Panels
The panels form the primary structure of a garage door and contribute to its strength and durability. Panels offer protection against the elements and potential intruders. Additionally, they contribute to the aesthetic appeal of your home, as they are available in a wide range of styles and designs.
Panels are typically constructed from materials such as steel, aluminum or wood. Some panels offer insulation options, helping to regulate temperature and enhance energy efficiency.
Tracks
Tracks are typically made of galvanized steel and facilitate the opening and closing motion. They have three different components — the vertical tracks on either side of the door opening, the horizontal tracks overhead and the curved tracks that connect the vertical and horizontal tracks. Depending on the space, you might have a standard, pitched, low-headroom, high-headroom or vertical track configuration.
Correct installation and alignment of the tracks allow the door to operate smoothly and prevent any binding or jamming. Regular inspection and maintenance of the tracks, including cleaning and lubrication, ensures optimal performance.
Springs
Garage door springs are responsible for counterbalancing the weight of the door. There are two main types of springs:
- Torsion springs: These springs are typically mounted horizontally above the door. They store energy as they twist and release it to facilitate smooth movement.
- Extension springs: Unlike torsion, extension springs are installed vertically along the sides of the door. They stretch and contract to support the door’s weight.
Ensure that springs are correctly calibrated and balanced for safe operation. Regular inspection, maintenance and, if necessary, professional adjustment or replacement of springs prevent potential accidents or damage.
Rollers
Rollers are small components that allow the door to glide smoothly along the tracks. They are typically made from nylon, steel or durable plastic materials. The choice of roller material depends on factors such as noise reduction, durability and cost. Nylon rollers are known for their quiet operation and resistance to rust, while steel rollers offer enhanced durability. Plastic rollers are an economical option but may wear out faster.
Hinges
Hinges allow the door sections to move independently while maintaining stability and alignment. Hinges provide the necessary pivot points for the door’s sections to move smoothly during operation. Standard hinges connect adjacent panels, while center hinges connect the door’s sections to the vertical tracks.
Insulation Options for Comfort and Energy Efficiency
Insulated garage doors provide a barrier against extreme temperatures, reducing heat loss during the colder months and minimizing heat gain during the hotter months.
Types of Insulation Materials
Various insulation materials are commonly used in garage doors, each offering different levels of thermal efficiency and soundproofing capabilities. Here are a few common types:
- Polystyrene: This insulation consists of rigid foam panels inserted into the door’s construction. It provides good thermal resistance and helps reduce noise transmission.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane is known for its thermal performance and structural integrity. It involves injecting foam insulation into the door’s panels, creating a solid layer that bonds with the door. Polyurethane insulation provides excellent energy efficiency, noise reduction and added strength to the door.
- Reflective insulation: This type of insulation is a radiant barrier material that reflects heat. It consists of layers of aluminum foil laminated to insulation materials like foam or cardboard.
Weatherstripping for Protection Against the Elements
Weatherstripping is a sealing material installed along the edges of the door, creating a tight barrier against external elements, such as:
- Temperature: Sealing gaps and minimizing air infiltration helps prevent the intrusion of cold air during winter and hot air during summer. This insulation reduces the strain on heating and cooling systems, leading to energy savings and increased comfort.
- Moisture: Weatherstripping forms a barrier against moisture, preventing water and humidity from entering the garage.
- Pests: Weatherstripping helps keep pests like insects and rodents at bay by sealing off potential entry points.
Types of Weatherstripping
Several types of weatherstripping materials are available, each with its advantages and considerations.
- Vinyl: Vinyl weatherstripping is resistant to weather conditions, including sunlight and moisture. They are easy to install and provide effective sealing against drafts. They can be used for sealing the sides and top of the garage door.
- Rubber: This type of weatherstripping is typically made from Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) and offers flexibility and sealing properties. It is resistant to extreme temperatures and remains pliable over time. Rubber strips, gaskets or bulb seals are commonly used for the bottom of the garage door, creating a tight seal against the floor.
- Brush: Brush weatherstripping consists of bristles or filaments attached to a flexible metal or plastic base. The bristles create a barrier against drafts, dust and pests while allowing for easy movement of the garage door.
- Pile: Also known as fuzzy weatherstripping, features a strip of fine fibers attached to a backing. The fibers compress when the door closes, creating a seal against drafts and insects.
Additional Features and Accessories
In addition to what the parts of a garage door are called, various additional features and accessories can enhance convenience, security and functionality:
- Opener: An opener system is an addition that automates the operation of your garage door. The parts of a garage door opener system consist of a motor, a drive mechanism and a remote control or keypad for easy access. Opener systems often include safety features like an automatic reversal, which prevents the door from closing on objects or people in its path.
- Lighting: Installing adequate lighting in the garage enhances visibility and safety during nighttime use.
- Keypads: Keypads mounted outside the garage allow keyless entry, enabling family members or trusted individuals to access the garage.
- Battery backup: A battery backup system ensures your garage door remains operable during power outages.
Choose Quality and Expertise for Your Garage Door Needs
When it comes to finding experts in the industry contact R&R Doors. As a family-owned business with a legacy dating back to 1986, we have established ourselves as a trusted name in the industry.
Whether you’re seeking a new garage door installation, repairs or expert advice, R&R Doors is here to provide you with the utmost professionalism and customer satisfaction.
Take the first step towards a superior garage door experience by contacting R&R Doors today.

